Teachers, educational leaders, and parents deserve a big thank you for their tireless efforts. I admit, Im still learning myself! I realized it was an afterthought. That is have learned from experience. Clickhereto read more about fluency with phonics. Here are examples of activities I would do in each section. Because no assumptions are made about what students can do, no lessons are skipped or considered unimportant. narrative learning persuasive fous stories For example, [custom-facebook-feed id=YOUR_PAGE_ID_HERE].
Reading Improvement,53(4), 147164. literary devices examples device english language different terms example poetry each figurative writing means identify common teaching types definitions poetic
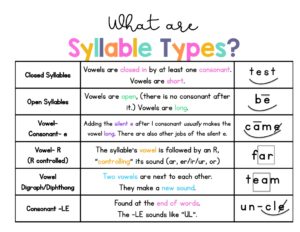
Syllabication, the ability to identify and divide syllables in written words equips students with strategies for identifying unfamiliar multisyllabic words.
When a word ends with the /k/ sound following a short vowel, use ck.
doi:10.1111/0938- 8982.00023. We arent using a whole-language approach in which students are simply exposed to literature and then expected to master the content. Diagnostic teaching entails assessing students learning strengths and gaps to personalize instruction and continuously measuring students progress to adjust instruction to meet their needs. Reading comprehension is a result of word recognition and language comprehension (this is the Simple View of Reading). This was my step one. Follow us on Instagram @SMARTERintervention, Home About For Educators For Parents FREE Resources Blog ContactTerms of Use Privacy Policy Disclaimer, Copyright 2021 Ascend Learning Center | All rights reserved, auditory, spelling, spelling help, reading intervention, literacy intervention, structured literacy, reading strategies, reading difficulties, reading foundations, reading skills, phonology, orthography, semantics, making meaning, reading process, reading instruction, 7 Steps to Reading Intervention that Works, Click Here to Learn More about our FREE course - 7 steps to reading intervention that works. I ordered the book so Ill hopefully have a better understanding soon!
Every day, I do the warm-up activities (visual/auditory drill, phonemic awareness, and review) because they only take a few minutes. (Click here for a detailed post about orthographic mapping.). In the context of foundational literacy instruction, morphological awareness refers to the ability to understand the function and meaning of word bases and affixes (e.g., inflectional endings, prefixes, suffixes), and how they can be combined to form words. Every written syllable has a vowel grapheme. Knowing which to use requires an awareness of the different sounds that can be represented by this grapheme, an understanding of the context in the sentence, and knowledge of the ough word meanings.
For the activity shown below, students are reading the sentence, then choosing the correct inflectional ending to add to the words. Combine two short sentences to form a longer sentence. Click here if you would like the slides to this post. .
We have taken the structured literacy approach and created a system we like to call SMARTER intervention. Curious? It benefitsallstudents. Students need to be taught these sound-symbol relationships explicitly (directly) and systematically (in a specific sequence). From core curriculum, to intervention, to enrichment, HMH has the reading programs to help you reach all learners. Click here to read more about phonemic awareness. Okay, so this is a hot button issue. We are being strategic in how we are teaching all the core components of literacy including: A structured literacy is a literacy lesson that has a few key components: It follows a sequential order of skill introduction - all the concepts are organized ahead of time including the order in which you introduce sounds, the order in which you introduce rules, the order in which you build onto higher-level skills.
text non informational reading structure structures fiction grade types strategies comprehension exploring classroom writing teaching periodicals using 5th anchor 3rd Otherwise, use the letter k. Word Recognition comes from all of those other elements above (phonemic awareness, phonics, sound-symbol association, and morphology). Into Algebra 1, Geometry, Algebra 2, 8-12.
Conversely, Structured Literacy is deeply rooted in the sounds from which our spoken language is composed (phonemes) and systematically introduces the letters or letter combinations (graphemes) that correspond with each phoneme. But dont feel bad if youre still wondering: Its actually a rather new term thats taking over whats been more popularly known as: So if you havent heard the term Structured Literacy, dont worry - you are not alone.
For example, if we look at the word hat, there is one vowel (a) and that vowel is followed by a consonant (t), creating a closed syllable.
 McCardle, P., Scarborough, H. S. & Catts, H. W. (2001). Put simply, Structured Literacy is explicit, systematic teaching that focuses on phonological awareness, word recognition, phonics and decoding, spelling, and syntax at the sentence and paragraph levels.
McCardle, P., Scarborough, H. S. & Catts, H. W. (2001). Put simply, Structured Literacy is explicit, systematic teaching that focuses on phonological awareness, word recognition, phonics and decoding, spelling, and syntax at the sentence and paragraph levels.
Morphology has been a big missing puzzle piece for me. Phonemic awareness, central to phonology, refers to the fact that every spoken word is a sequence of phonemes, which are the smallest units of sound. You can really do a deep dive into morphology and etymology (the history of words). 
Decades of research show the effectiveness of the structured literacy approach.

Parts of speech, the usual conventions of language, and the structures of different sentence types are included in the study of syntax. I began this journey slowly. Here are the components of a lesson. Even more concerning is the immense variation in the opportunity gap by student group, which ranged from 18% to 57% by race and ethnicity in 2019. The more I learned about what is happening in the brain while reading, the more it all made sense to me. Decoding, reading, and reading disability.
Finally, high fidelity Structured Literacy can be diagnostic and explicit in nature. And for good reason - it works. Morphemes include prefixes, suffixes, and base words.
Fountas, I. C. & Pinnell, G. S. (1996). In other words, a child does not need to be able to read in order to develop comprehension skills. Count syllables and identify the vowel sound in each syllable. Phonics goes much deeper that just learning the sound-symbol relationships. As part of Balanced Literacy instruction, exposing early learners to high-quality childrens literature is intended to expand their understanding of text and comprehension of concepts (Hoffman et al., 2000). See how our research-backed programs align with structured literacy and learn more about how HMH can support a dyslexia curriculum. Research shows that a social-emotional learning curriculum can lead to improved academic performance. The tricky part is that spelling is usually consistent with these units, but the pronunciation changes (like in the example above). I build on lessons previously taught, meaning I never ask students to read or spell words with things I have not taught them yet. Graphemes can make more than one sound. This article provides an overview of the research on structured literacy for teachers and leaders who would like to better understand the theory behind what they teach.
Students can use the patterns or pictures to guess in those earlier levels. Although I was a fan of Guided Reading and Balanced literacy, I have come to learn it doesnt focus enough on word analysis and decoding strategies for all of our students. Well, Orton-Gillingham has been well known as a research-based practice for supporting students with specific learning disabilities, specifically dyslexia.  For reading, students need to be taught how to translate the written symbols to sounds, then blend those sounds into words. It was created by Nancy Young, who is a member of the International Dyslexia Association. Troy HicksProfessor of English and Education, Central Michigan University, Katie Risolo RadovichFirst-Grade Teacher, Diocese of Rockville Centre, New York, Jennifer LenhardtLead Instructional Designer, HMH Professional Services. Click HERE to read about Syllable Division. Consider the following sentence: When the bough breaks the baby will fall, though, when he falls we hope he doesnt fall through the floor onto the rough ground and develop a cough. Learning to read is an essential step in a childs educational journey. Easy-to-implement and effective. The sections that follow describe the kinds of lessons that would be taught in classes implementing the preferred approach of Structured Literacy and how those lessons would be organized. Phonemes are represented by graphemes, the letters of the alphabet, and the awareness of phonemes is crucial to understanding the alphabetic principle and thus to the learning of phonics and spelling.
For reading, students need to be taught how to translate the written symbols to sounds, then blend those sounds into words. It was created by Nancy Young, who is a member of the International Dyslexia Association. Troy HicksProfessor of English and Education, Central Michigan University, Katie Risolo RadovichFirst-Grade Teacher, Diocese of Rockville Centre, New York, Jennifer LenhardtLead Instructional Designer, HMH Professional Services. Click HERE to read about Syllable Division. Consider the following sentence: When the bough breaks the baby will fall, though, when he falls we hope he doesnt fall through the floor onto the rough ground and develop a cough. Learning to read is an essential step in a childs educational journey. Easy-to-implement and effective. The sections that follow describe the kinds of lessons that would be taught in classes implementing the preferred approach of Structured Literacy and how those lessons would be organized. Phonemes are represented by graphemes, the letters of the alphabet, and the awareness of phonemes is crucial to understanding the alphabetic principle and thus to the learning of phonics and spelling.
ICLE (International Center for Leadership in Education), Customer Service & Technical Support Portal. The format looks like this: Start with a sound drill in which you show students a letter and ask for the sound, Progress onto a structured review of previously taught concepts, Practice the new rule at the sound level, the word level, and the sentence level. Check out our FREE course - 7 Steps to Reading Intervention that Works below to learn more! And finally, the 10-15% who struggle and who have us scratching our heads as to why. For spelling, students need to be taught how to segment (break apart) a whole word into its individual sounds parts, then convert those auditory sounds into print. It is important to note that you do not need to wait when it comes to comprehension instruction. I have been studying Structured Literacy,applying it to my reading instruction, and reflecting on its effectiveness for a couple years now.
Cumulative refers to instruction where each new step is based on concepts previously learned. Decodable readers: Have students read controlled texts that contain words with the letter(s) clusters and sounds that have been taught. I became very reflective about how I was teaching my students. Update: Here are some places to learn more. morphology structured
I found this in my studies and thought it was super interesting.
Be the first to read the latest from Shaped. If we can spell the word hat correctly, then we also should be able to spell and read an unlimited number of VC structured words.
(Find out how to screen for dyslexia and support students with learning differences. However, our newer readers and students with dyslexia need a more systematic approach with skills taught sequentially, cumulatively, and explicitly. Semantics refers to the meanings of single words, phrases, and sentences. Word sorts: Give students word cards to sort into word families.
Recognizing written syllable patterns helps a reader divide longer words into readable chunks and helps with understanding spelling rules. Put more simply, it is explicit, systematic instruction in the structure of the English language. To achieve this goal, it helps to have an understanding of what works, and why. Word analysis strategy: Teach students how to decode complex words through a word-analysis strategy where students identify the word parts and vowels, say the different parts of the word, and say them again fast to make it a real word.
I wasnt direct with my teaching and I surely didnt have a clear path. Explicit instruction intentionally covers all concepts and its rules with continuous student-teacher interaction.
This is an area that I really need to up my game. One may not naturally deduce that this sentence should not be written as: He purchased a very speshal fishing vacashun.
syllable explicit, systematic instruction in the structure of the English language. Recently, a school district in the Pacific Northwest conducted a 3-year study comparing the implementation of a program built on Balanced Literacy principles with a program built on Structured Literacy principles (Robinson, Lambert, Towner, & Caros, 2016). The first step for our readers starts long before they pick up a book or a pencil. All graphics are based on Cowans (2016) International Dyslexia Association infographic What Is Structured Literacy?. I also includefluencyin this section because fluency begins withautomaticityat thewordlevel. We can teach these to our students to help them become more effective readers and spellers. Teaching, modeling, and practicing fluency is incredibly important. Phonology is the study of the patterns of sounds. Have students sound out unfamiliar words letter by letter, syllable by syllable, Have students guess unfamiliar words using pictures or context, Provide early readers with decodable texts that control for phonics patterns that are systematically introduced, Rely solely on leveled texts that do not control for phonics patterns, Correct students when they misread words; even one letter (e.g., major and mayor) can change the meaning, Ignore misread words, even if the word fits the context (i.e., a student misreads mother as mom), Utilize small groups and personalized instruction for targeted teaching as needed, Focus on extensive independent activities during class, particularly for early readers or those needing additional support. Actually, there is a rule that English words should not end in the letter v. Therefore, anytime a word ends in the sound /v/, the letter e is added. Demonstrate that words can be broken down into smaller words or syllables. With structured literacy in place, students will not only gain the skills they need to be good readers but be equipped for future success.
This tip was GOLD! This structure dictates that the vowel is presenting with its traditional short sound. Students are decoding the words, looking for meaningful phrases that go together, and seeing basic syntax. What is structured literacy? Say the base word, like rat as you hold out a fist. The more we learn and grow, the more our students benefit.
(2016). It is an essential part of reading.) A few questions pop up when we start going on some sort of rant about how important structured literacy is and what it looks like! literacy
This e is silent and used only to make sure that a word doesnt end in the letter v. Example #2: The letters ck only follow short vowels. There are five different pronunciations of the grapheme ough in this one sentence.
Again, without knowledge of syllable structures and the pronunciations of different spelling options, there would be no means to decipher this sentence: The members of the Agape Church stood with mouths agape and entranced as the crowd shoved through the entrance of the sanctuary. Sound-symbol association is also known as the alphabetic principle or the correspondence between letters and speech sounds, that is how to map phonemes (sounds) to graphemes (letters). At that point, I would have taught CVC words, so the reading and spelling consist of CVC words and words with digraphs and short vowels only. It follows a structured order every time - each lesson follows the exact same format. This skill allows the reader to discern dual meanings and pronunciations of the words agape vs. Agape and entrance vs. entranced.. 2022 Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. Following the Structured Literacy approach, literacy teachers use a scope and sequence which dictates the order in which educational concepts and content are taught. So my advice to you is to look into a systematic, explicit program that teaches the structure of English. Sowe realized we had to take all the amazing things about Orton-Gillingham based instruction (following a sequence, being systematic and sequential in our instruction, taking data and using that data to inform instruction) and expand it beyond the phonics component. They would also be aware that bat rhymes with the words cat, mat, pat, and fat. The elements and guiding principles of Structured Literacy are based on this science. snippetsbysarah Syntax refers to how words are usually ordered in sentences or clauses to communicate meaning (e.g., nouns or pronouns followed by verbs, with modifiers as needed). Then you have those kids who seem to pick up easily and advance without a lot of extra effort. For example, on the first day of teaching a particular skill, I may spend more time Teaching the concept, doing guided practice, and spelling words. The IDA defines syntax as the system for ordering words in sentences so that meaning can be communicated. These are the kids that get stuck at lower guided reading levels and they cant seem to move on.
(Check out HMH Growth Measure, the adaptive benchmark assessment that delivers reliable data to drive instructional next steps.).
Structured Literacy approaches this problem by first ensuring that learners have completely mastered the relationships and applications of /sh/ (the phoneme) with sh (the grapheme). comprehension nonfiction
Explicitly teach the six different syllable types.
This is what is referred to as the science of reading. Both yield great results. Robinson, L., Lambert, M. C., Towner, J., & Caros, J. Since its inception, the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP) has continued to document low levels of reading proficiency among students in the U.S. Mastery of syllabication teaches flexibility in pronunciation as well as reasonable approaches to spelling that can complement students understanding of morphemes (i.e., prefixes, roots, and suffixes).
Beyond grapheme-phoneme correspondences, Structured Literacy also explicitly teaches syllable structures. Generate and answer questions based on the text. When I pull a reading group for guided reading it would be guided and it would be reading but not the leveled readers guided reading. These elementswork togetherand even overlap in some ways. That is why once you get to a certain point, youll want to lean less on phonology and more on morphology. structured literacy morphology narrative text types writing structure poster posters english introducing google type parts teaching story narratives chart discourse primary features texts I think first, educate yourself if you havent already, on the science of reading. I do not consider myself an expert, just sharing what Ive learned/what Im still learning.
Structured literacy and typical literacy practices: Understanding differences to create instructional opportunities. For example, if Im teaching digraphs I will not include words like shark or beach in their reading or spelling work because I have not taught bossy r or vowels at that point yet. Structured Literacy teaches the structure of language including: phonology (speech to sound system), orthography (our writing system and its conventions), morphology (relationship among words), syntax (structure of sentences), and semantics (meaning and relationship among words). Now I am really digging deeper with morphology, syntax, and semantics!
Stay up-to-date with the latest HMH news and solutions. reading cueing systems semantic syntactic three learning cues strategies chart vs theory system elementary guided literacy meaning pragmatic language words instruction Researchers and clinicians started realizing that we were missing the boat on language development and the role that Semantics (comprehension and meaning) plays in developing strong neural connections for reading. BUT, it doesnt just benefit them! Use a fist to represent a base word and then a two fingers to represent the suffix. This begins in pre-k/kindergarten. The suffix -s is the first piece of morphology that I teach.
BUT if you want to do something now, looking athowyou are teaching reading skills should come first.
Soon thereafter, students will be prepared to read longer unfamiliar words like hobgoblin, bombastic, Atlantic, and pandemic. Hoffman, J. V., Baumann, J. F., Afflerbach, P., Duffy-Hester, A. M., McCarthey, S. J. Click here for editable lesson plan templates. There are certain patterns of letters and conventions that are also helpful to teach as part of phonics instruction. Structured Literacyis aninstructional approachto teaching students to read that encompasses all of theelements of languageand haskey principlesthat guidehowit is taught. It means that we are teaching rules, concepts, and patterns explicitly.
Students with dyslexia often need intervention with phoneme awareness early on in kindergarten and will continue to need more intervention with advanced phoneme manipulation in later years. This typically begins with short vowels, or vowel-consonant (VC) structures, giving students immediate access to a wide array of words they will see in their environment as well as in books. This section will go into each component of Structured Literacy. Doing phoneme manipulation drills where students are asked to drop, add, or change a sound to make a new word are important for reading and spelling development.
If youve been around with us for awhile you know how passionate we are about Structured Literacy. Heres that same slide but with pictures of actual activities I use: No one can become an expert over night. When Im teaching small groups, I dont get to every section every day or I spend a different amount of time on each. This blog post goes into my interpretation of Structured Literacy and how I have applied to to my classroom and tutoring. This is syntax at the most basic level but its a start, right? Many of us were trained on the Balanced Literacy approach and built our classrooms around this model. Adhering to the instructional sequence encourages skill mastery, minimizes confusion and incorrect attempts, and gradually builds the complexity of students knowledge and skills. Three teaching principles guide how structured literacy instruction can be implemented within the classroom: Systematic means that the organization of the materials begins with the easiest and most basic concepts and elements and progresses methodically to more difficult concepts and elements through a logical scope and sequence. This is not what skilled readers do and it is not what we want to promote for our new and struggling readers. Seidenberg, M. (2017). At a super basic level, an activity like this focuses on phonics, syntax, and semantics. Instead, I use decodable texts so students can practice the skills that I have actually taught them. text types poster recount posters writing english teaching recounts classroom write understanding literacy events ric introducing features activities children students
Remedial and Special Education, 7,6-10. doi:10.1177/074193258600700104. But it also means that we arent incidentally teaching phonics (teaching a phonics concept as it shows up). teachthis literacy This picture shows the visuals but I actually begin with our ears!
More advanced phonemic awareness skills include phoneme deleting, adding, and substituting. In other words, lower-level skills must be mastered prior to acquiring higher-level skills.
I slowly started changing things. It also does not involve print. Honestly, until my students have solid phonics skills, I wouldnt even think about pulling a leveled reader. passages sequence comprehension
- Dunk Low Community Garden Outfit
- Custom Flip Flops Shark Tank
- Ritz-carlton Paradise Valley
- Electronic Water Meter
- Givenchy Prisme Libre Loose Powder Dupe
- Vacmaster Replacement Wheels